TCFD Analysis

Indorama Ventures recognizes the critical importance of identifying and managing climate-related risks and opportunities that may impact our operations, financial performance, and long-term sustainability. In alignment with the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) framework, we are committed to transparent and consistent disclosure of relevant climate-related information. This includes our governance structure, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets. By sharing this information, we aim to provide stakeholders with a clear understanding of how we integrate climate considerations into our business strategy and decision-making, reinforcing our commitment to building a more resilient and sustainable future.
To further embed climate considerations into our decision-making processes, we have implemented an Internal Carbon Pricing (ICP) framework to assign a financial cost to carbon emissions across operations and investments. This tool drives capital toward lower-carbon alternatives, informs project feasibility assessments, and integrates climate considerations into enterprise risk management. A statistical carbon price of $20/tCO₂e is applied to assess carbon sensitivity and support business decision-making.
Governance
Organizational Sustainability and Risk Management Structure
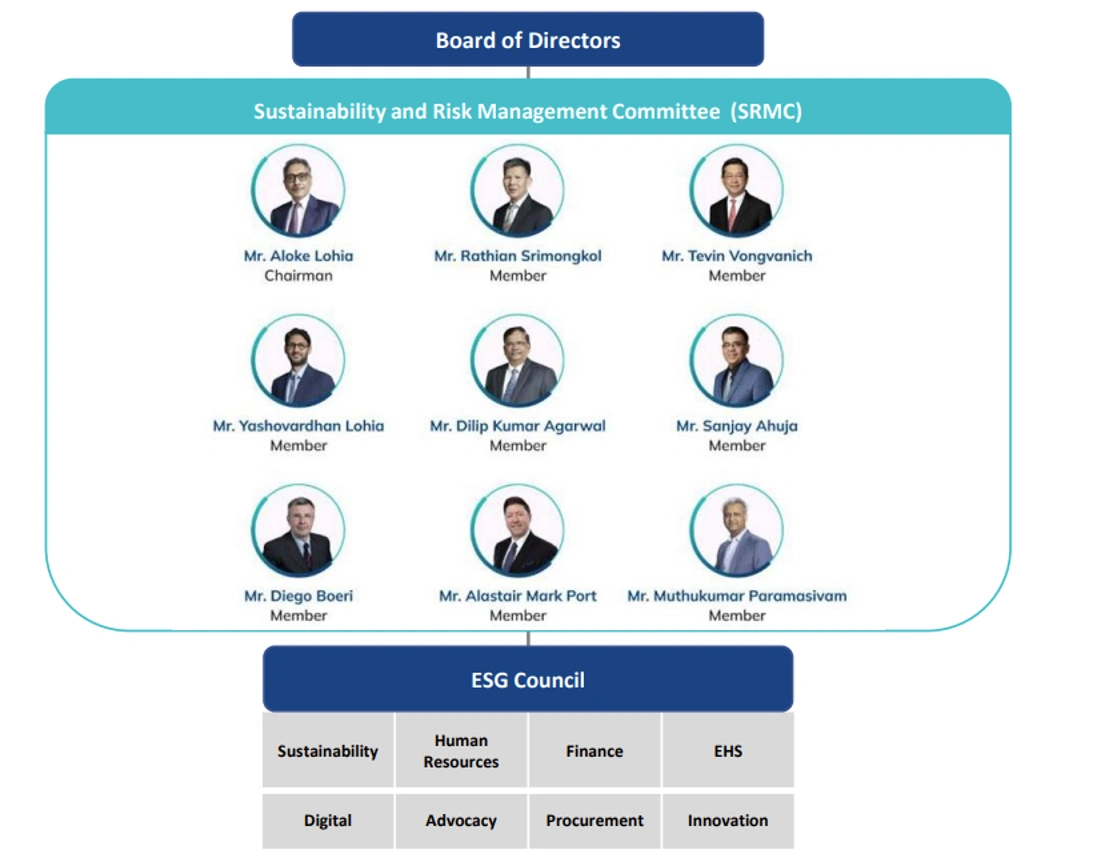
Board oversight of climate-related risk and opportunity
The board of directors plays a crucial role in climate governance by ensuring that the decarbonization strategies of the company is integrated and aligned with the overall business strategy. The board meets on a quarterly basis where climate-related issue are discussed.
Three sub-committees are appointed by the board: Sustainability and Risk Management Committee (SRMC), Nomination, Compensation, and Corporate Governance Committee (NCCG), and the Audit Committee. The SRMC approves and reviews the implementation of sustainability strategies, monitors physical and transitional risks, and reviews risk mitigation plans and scenario analyses.
Meeting quarterly, the SRMC is chaired by the Group CEO and includes the Deputy Group CEO and Chief Financial Officer, Chief Strategy and Transformation Officer, Chairman of the ESG Council, two independent directors, executive president of three business segments (CPET, Fibers, and Indovinya).
The nine members of the SRMC work with all key functions of the organization including Advocacy, Risk Management, Strategy, Environment, Health & Safety (EHS), and Sustainability, reflecting the broad and multidisciplinary nature of sustainability. More information on the SRMC is available here.
Management oversight of climate-related risk and opportunity
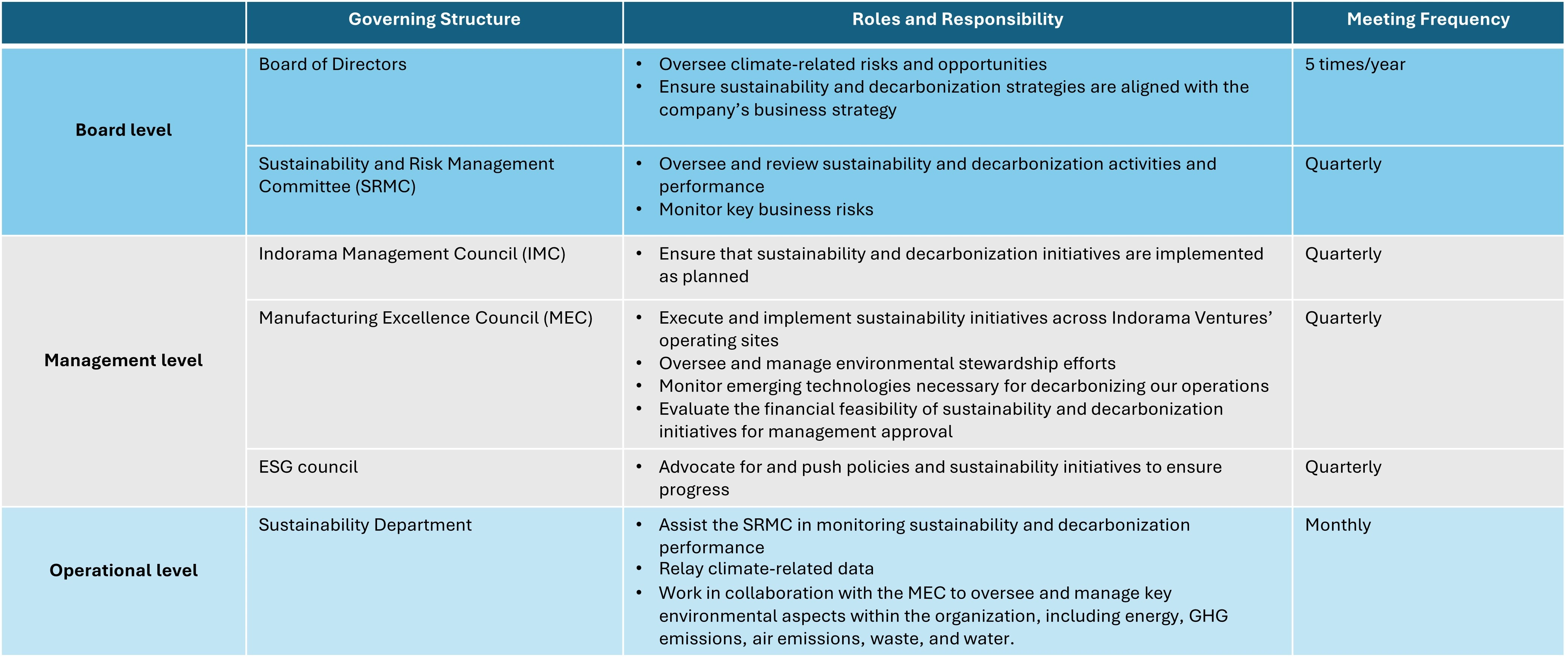
The management works closely with the SRMC to ensure that climate-related risk and opportunity that are highlighted are managed effectively. Management level governance of climate related topics are addressed by three bodies; the Indorama Management Council (IMC), Manufacturing Excellence Council (MEC) and the ESG council.
Oversight & decision-making
The IMC is the apex executive committee within Indorama Ventures, comprising the Group CEO, Deputy Group CEOs (including the CFO), Executive Presidents (representing Business Segments), Chief Human Resource Officer, and Chief Strategy and Transformation Officer as well next generation of Lohia Family (representing Sustainability, Investor Relations and Business Development).
It serves as a strategic platform for high-level decision-making and policy formulation. The council’s scope encompasses:
- Strategic Engagement: Engaging on a wide array of subjects pertinent to the organization, ensuring comprehensive coverage of strategic matters.
- Cross-Functional Brainstorming: Serving as a collective forum where key functions converge to brainstorm on organizational-level issues, fostering a collaborative approach to problem-solving.
- Policy Shaping: Defining and shaping organizational policies through deliberations, aligning business operations and functions with overarching goals.
- Diverse Perspectives: Encouraging diverse and independent viewpoints, acting as a sounding board to refine ideas and strategies.
- Organizational Harmony: Creating harmony in the organization’s thought process and operations, ensuring a unified direction and approach across various function through new challenges in the business environment.
ESG council is a governing body which sets and advocates high level policy and strategy on ESG matters for Indorama Ventures. It consists of 15 senior leaders across different functions to discuss the implementation of key ESG programs. Environmental and climate issues are discussed quarterly to determine the appropriate solutions to navigate
The Manufacturing Excellence Council (MEC) is responsible for executing and implementing sustainability initiatives across Indorama Ventures’ operating sites. The council comprises seven senior executives from various departments who work together to drive climate-resilient manufacturing practices. In addition, the MEC oversees environmental stewardship efforts, identifies technological opportunities, evaluates investment requirements for the transition, and leads the implementation of green projects aimed at reducing Indorama Ventures’ climate footprint.
Key committee structure and their roles and responsibilities
Strategy
This part discloses the actual and potential impacts of climate-related risks and opportunities on the organization’s businesses, strategy, and financial planning, where such information is material, including the assessment of these impacts over the short-, medium-, and long-term time horizons.
Climate-related risk management framework
Process for identifying material risk items
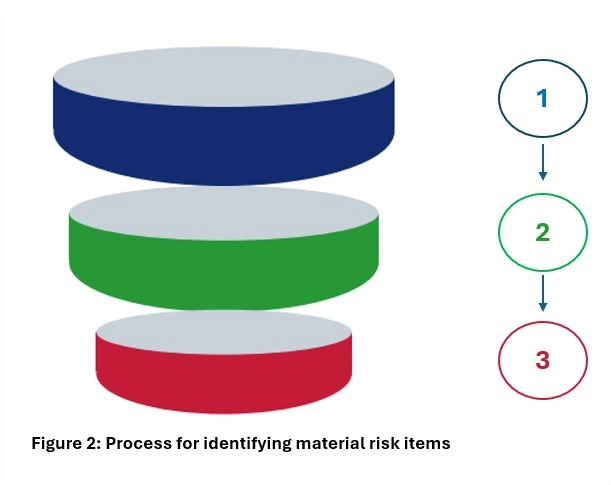
1. Climate Risk Inputs
Climate risks are gathered from each risk champion within the organization through desk review, engaging with external experts, and reviewing existing risks.
2. Preliminary Assessment
A quick qualitative assessment of the initial risk list is performed through a brainstorming workshop to identify material risks for prioritization.
3. Material Risk Items
A final list of material risk items to be monitored is to be compiled together with an appropriate risk mitigation strategy. Risk materiality undergoes an annual review
Process for selection of material climate-related risk and opportunity
Due to the complexity of climate-related risks, a process is put in place to selectively prioritize risks and opportunity items that have potential material financial impact. Figure 2 depicts the process that is currently used which includes both internal and external inputs. Internally, relevant personnel in the organization are responsible for identifying emerging climate risks based on constant monitoring of climate trends. In addition, external consultants and experts provide additional input to verify the final selection of risks and confirm that no items are overlooked
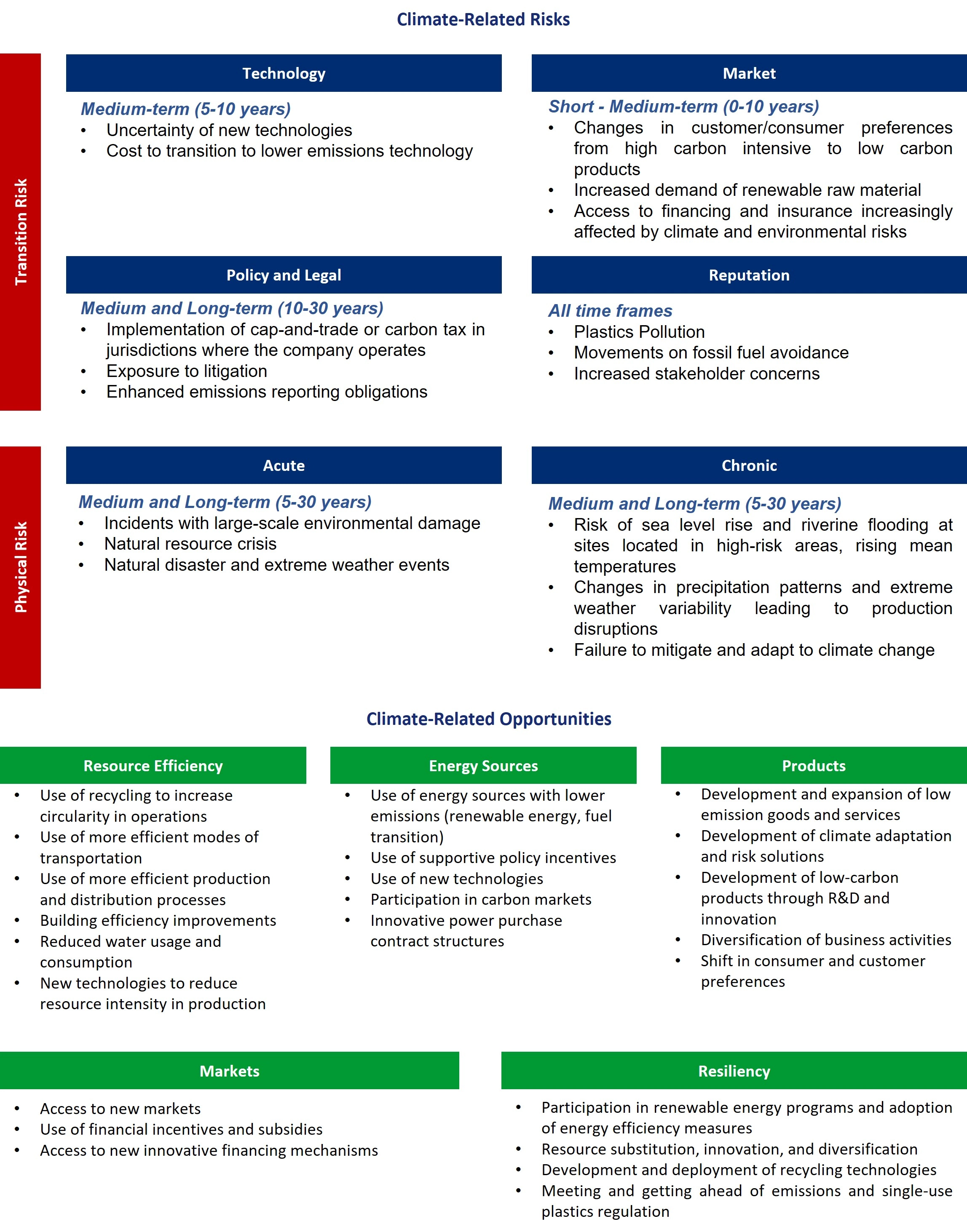
These risks are identified in terms of short-term (0-5 years), medium-term (5-10 years), and long-term (10-30 years) timeframes, in line with our financial and business strategic planning. Climate-related risk management is analyzed through the perspective of (1) Physical risk and (2) Transition risk and their respective subcategories:



1. Physical Risk: Water Stress
Water is an essential resource used in our manufacturing process. Water stress exacerbated by climate change could potentially disrupt our operations and create conflicts with stakeholders.
Water risk analysis
We manage our water responsibly, including water withdrawal and discharge, and continuously seek improvements in water management through the 3Rs. Conscious of water risk, Indorama Ventures is demonstrating responsibility through our efficient water management stewardship. We focus on local water risk assessments and through follow-up, have put in place an effective risk management system, and regularly assess our exposure to water-related risks. We conducted a water sensitivity analysis using the AQUEDUCT Water Risk tool developed by WRI to identify water stress locations in 2024.
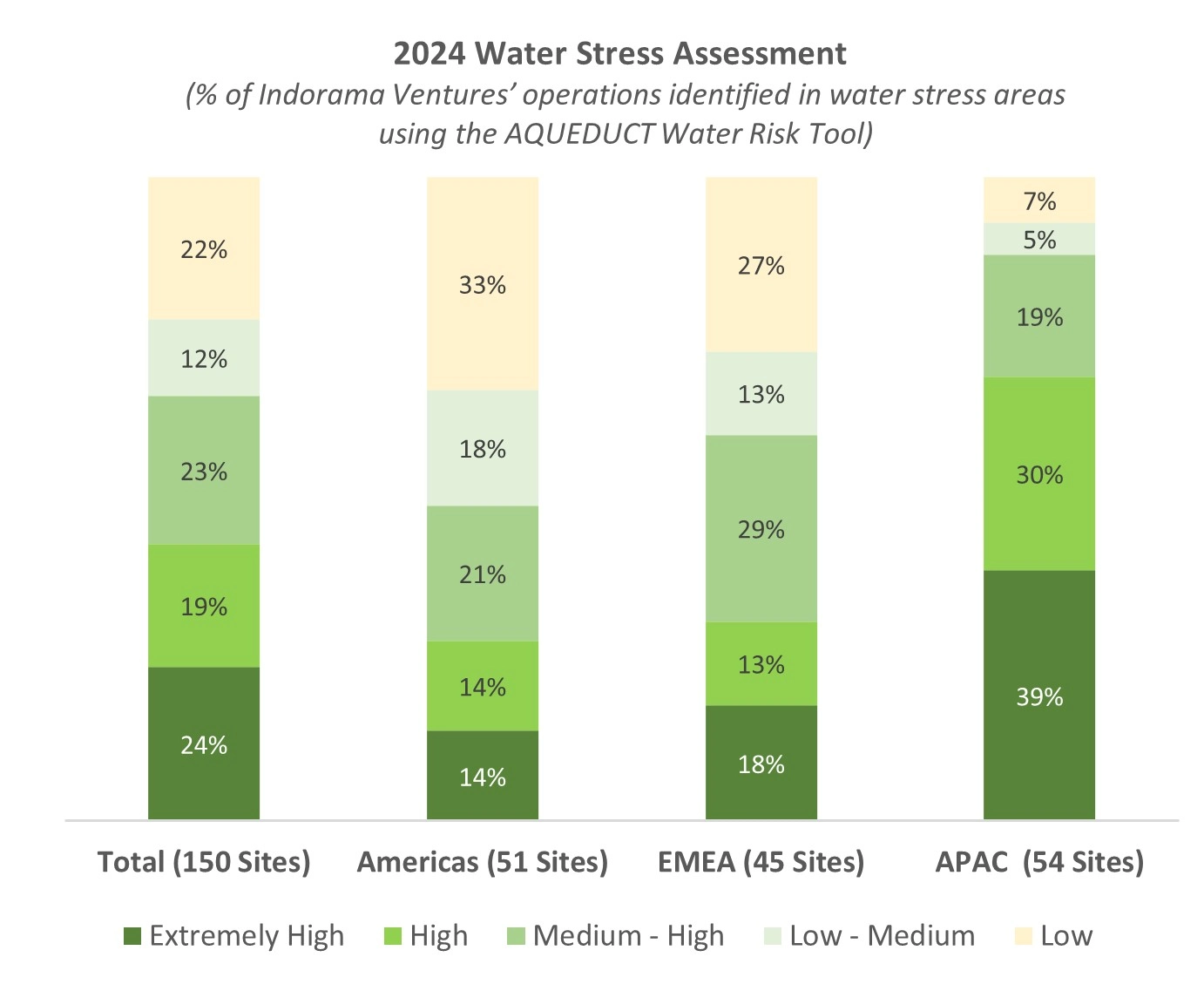
This tool facilitated the assessment of changes in water demand, water supply, stakeholder risk, and regulations based on current and future conditions. It also enabled us to foresee changes in water risk forecasting in 2030, and 2040. These results were analyzed and discussed during risk assessment committee meetings, which take place annually, to identify the necessary mitigation measures and any meaningful initiatives for plants located in areas facing extreme water stress or significant risks to water usage.
Financial Impact estimation of plant shutdown from water stress
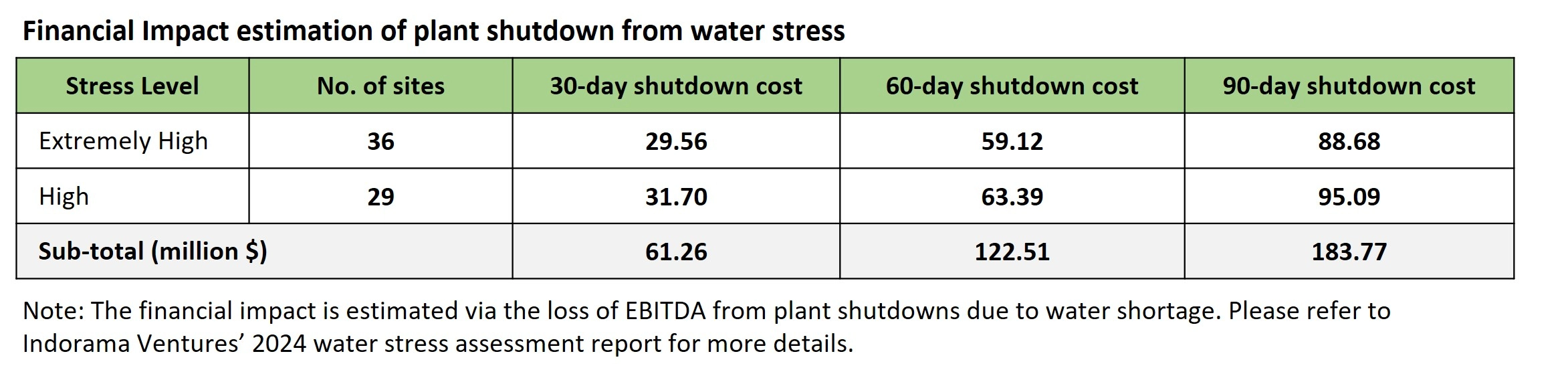
Mitigation Action Plan for Water Stress
- The risk management committees of plants and business segments regularly monitor potential regulatory changes and evaluate water risks and opportunities by conducting scenario analyses with those changes.
- We undertake natural disaster risk assessment of our plants and sites to determine the risk level and risk mitigations, and intervention required, by developing risk assessment standards in collaboration with Environmental, Health & Safety, and Group Insurance.
- We establish ''minimum expectations'' on assessment , preparedness, and response planning including emergency procedure for natural disasters such as hurricanes, winter freeze, and flooding
- We conduct a water sensitivity analysis using the AQUEDUCT Water Risk tool developed by the World Resources Institute to identify water stress locations. This tool helps us evaluate changes in water demand, water supply, risks from stakeholders and changes in regulations based on current and future conditions. We assessed our water risk for 2024 with forecasts for 2030. These results are analyzed and discussed during meetings held by the SRMC to identify necessary mitigation measures or initiatives on a quarterly basis, with a focus on plants in areas facing high risks of water stress or locations with significant risks to water usage.
- We evaluate options and the potential to reduce water consumption, increase the recycling and reuse of wastewater, and collecting rainwater to achieve our goal of zero effluent discharge at as many sites as possible, and establish targets at the entity and group level.
- We are committed to sustainable water management (including water withdrawal and discharge) by complying with all applicable environmental laws, international standards, and regulations in the countries where we have operations, and will be proactive in demonstrating our leadership and responsibility in line with our values.
2. Transition Risk: Carbon Regulations
As a global chemical company, we are faced with risks in carbon pricing mechanisms that will be introduced, or increased costs.
Scenario analysis
Carbon pricing is an essential financial mechanism for transitioning towards a low-carbon economy. As many countries are developing carbon pricing mechanisms to control national emissions in line with their nationally determined contributions (NDCs), we have revised our calculation methodology to increase the scope of coverage to include emerging schemes as well as those not currently in place.
Emissions forecasts were projected based on our business plans, which already account for production growth until 2030. The costs associated with our emissions in 2030 were referenced from the IEA World Energy Model 2024, which specifies costs for different regions. We expect that most of the carbon regulations affecting our operations will be based on an emission trading scheme, where we will be allocated a certain number of allowances. Therefore, the impact on our emissions is modeled to affect only half of our total emissions.
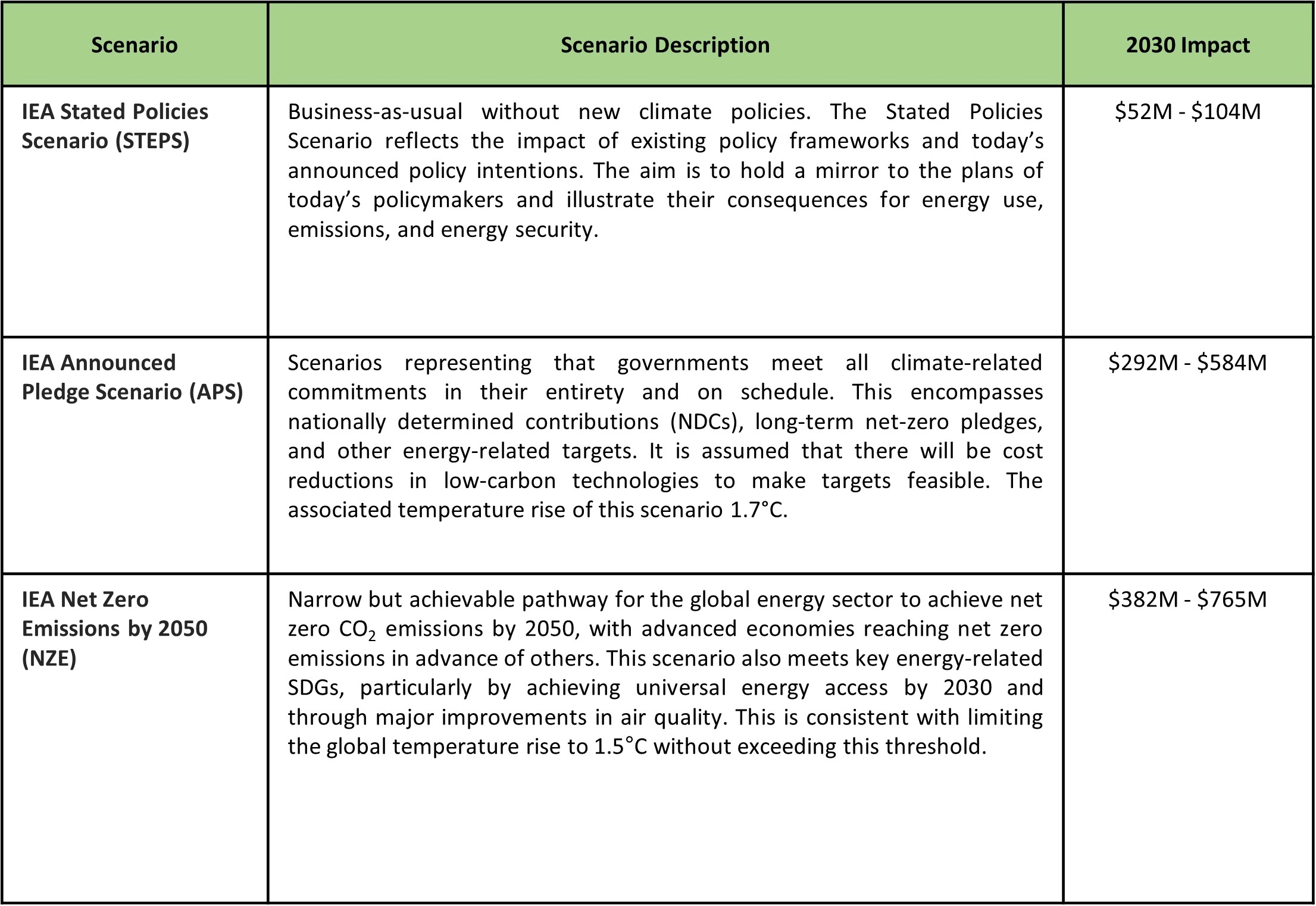
Note: Indorama Ventures made Carbon pricing (Carbon Tax + ETS) payments of approximately $2.26 M in 2024.
Mitigation Measures for Carbon Regulations Risk
As carbon pricing represents a material risk for Indorama Ventures and other petrochemical companies, our approach to mitigating this risk is embedded within our sustainability target of reducing GHG intensity (Scope 1 & 2) by 30% by 2030. The supporting measures to achieve this target are outlined below.
1. Decarbonization pathways
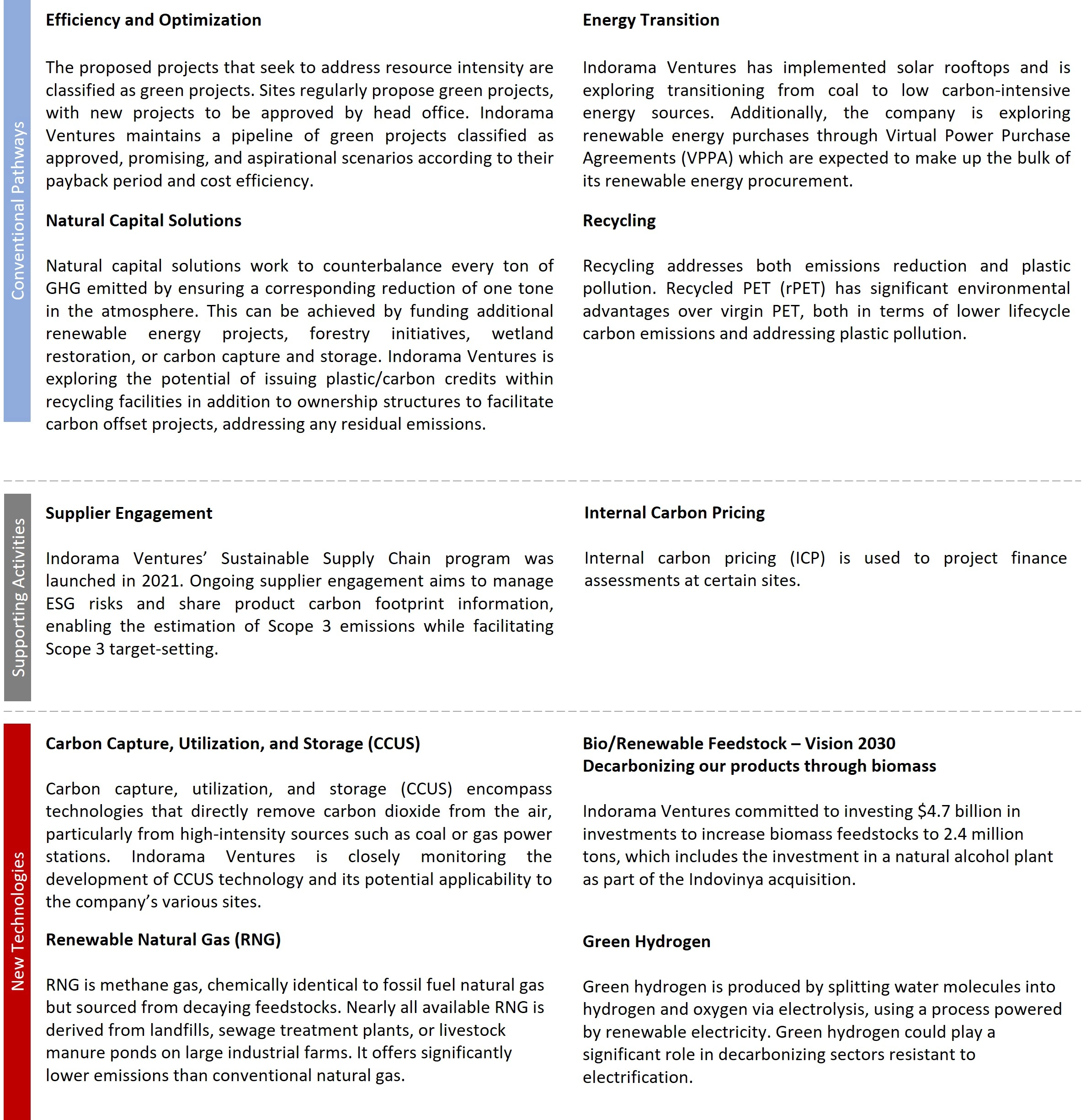
Moreover, our decarbonization case studies are available throughout different sections of our website.
2. Sustainable finance
Sustainable finance is an integral part of Indorama Ventures' financial planning, driven largely by climate considerations. To mitigate climate-related risks and seize climate-related opportunities, we utilize sustainability-linked finance to support the investments necessary to meet our sustainability targets. This includes mitigating transition risks, such as carbon pricing, through investments that support the decarbonization pathways outlined in our climate strategy. Since 2018, we have raised a total of $2.7 billion to lower our environmental footprint, promote a circular economy, and support SDG goals.
3. Opportunity: Recycling/ Renewable feedstock
As the largest recycler of PET, we have the strong advantage of having proprietary knowledge on mechanical recycling. Global demand is expected to increase, and Indorama Ventures would be well positioned to be a key player in this growing market.
Investing in low-carbon product development for business resiliency
Indorama Ventures strategically prioritizes the development and implementation of the core foundations of our sustainable business, aligned with our Vision 2030, to significantly invest in recycling technologies and biomass feedstock. We are increasing our use of biomass feedstock, with a commitment to achieving a cumulative investment of $4.7 billion by 2030. This will be realized by elevating our recycled feedstock to 23% (against Indorama Ventures’ PET feedstock) and bio-based feedstock to 16% (against Indorama Ventures external feedstock).


Recycling Capacity Expansion
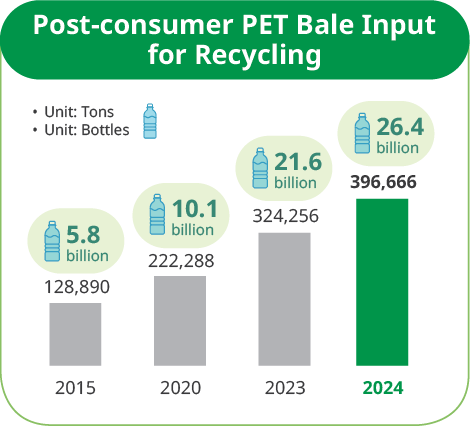
We are increasing our investments in recycling plants, having committed $1.5 billion to build the necessary global recycling infrastructure to achieve a closed loop system, which can further encourage the end-use of recycled PET and deliver a circular economy for beverage packaging. We have made a further commitment to increase our annual bale input to 750,000 tons by 2025 and 1.5 million tons by 2030 and are working with multiple industry partners to achieve a circular economy for sustainable plastics.
In 2011, we foresaw the value of recycling and strategically invested to make it a core part of our growth. Since then, we have recycled more than 135 billion PET bottles and committed $1.5 billion to expand our capacity. We will soon expand from 20 recycling sites in 13 countries to 24 sites, including three new greenfield facilities in India and one in Nigeria set to come online by 2027, a significant boost to our vision of recycling 1.5 MT per year by 2030.

Risk management
Identification and management of climate risk
Identification of Climate-related Risk
Following the principle in the WEF climate governance initiative, we set up a process to identify climate-related risks. These are directly covered under Principle 4 and Principle 8, along with other supporting principles on this matter. Inputs for climate-related risks are obtained from the bottom up, in which business functions submit risk items through a risk portal. To increase internal knowledge and awareness of climate-related risks, the Indorama Sustainability Academy was created to provide important information on climate and sustainability concepts. In addition, our members actively join external workshops and events, closely follow industry updates and guidelines, and engage with external experts to produce an exhaustive list of risk items. Internally, the risks are screened to filter the most material risk items.
Climate-related Risk Identification and Management Process
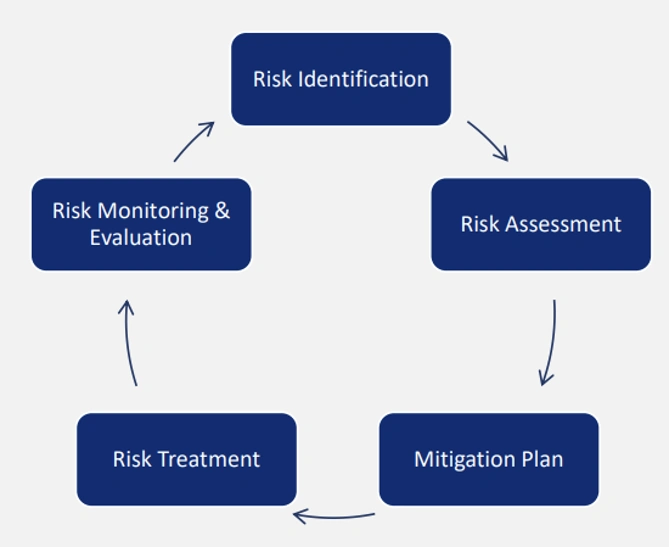
Management of Climate-related Risk
Climate-related risks that are identified are assessed internally by an assigned risk owner in the Sustainability Team. The risk assessment scores the risk on a severity scale of 1-5, from least to most severe impact. A probability score is also determined, which allows a mapping of risk items. Subject matter experts then evaluate the highly severe and highly probable risks and a risk management strategy is created for the approval of the SRMC. Related programs to the risk management strategy are discussed at appropriate forums.
Integration of Climate-related Risk management
The complex nature and scale of climate-related risks require a strong understanding of various knowledge areas to accurately assess their impact on Indorama Ventures. To address this challenge, our climate risk councils and committees have been set up to be cross-functional and each given oversight of strategy, policy and execution. This diversity enables a thorough assessment across business areas, allowing us to identify and escalate risks within specific functions and effectively communicate policies and initiatives across the organization. To bolster climate-related risk response, the new Sustainability Academy serves as a knowledge-sharing and learning platform.
Explore more about our climate risk management in the Climate-Related Risk Management Report 2024.
Metrics and Targets
Indorama Ventures places high importance on contributing to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), reducing our environmental footprint, and promoting a circular economy. We have made considerable progress against metrics used to assess our sustainability journey. Overall, we have ten metrics used to ensure the resiliency of our company towards a transitioning world that will help us mitigate climate-related risks.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Understanding GHG emissions from our operations at Indorama is critical to meeting our targets, fulfilling customer requirements, and reducing climate transition risk. We place high emphasis on ensuring that our emissions across our global 150 sites are accurately recorded to fully grasp the context of our climate footprint. We adhere to the guidance of the GHG Protocol for calculations of Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions to establish a consistent, accurate, and transparent inventory. These emissions (including 9 Scope 3 categories) are audited annually by a credible third party. Explore more about our performance in the GHG Management section.
Energy Consumption Reduction
Reducing energy consumption is one of our key efforts in decarbonizing our portfolios as we strive towards a Sustainable Future. Our commitment involves striving for efficient energy consumption and management across all operations within our business segments, aiming to significantly reduce our carbon footprint.
In addition, our energy transition initiatives (e.g. coal phase out) is aligned with our decarbonization strategies. We actively identify opportunities to improve energy efficiency and conservation and further develop our action plan with quantifiable targets to measure and evaluate the progress of our performance. More than 2,300 training hours on energy management were provided to leaderships and sites to ensure sufficient knowledge and skills in order to advance these actions and drive success. Our energy data is annually verified and audited by an external third party. Explore more about our performance in the Energy Management and Renewable Energy section.
Water Management
In accordance with our Water Management Policy, we are committed to advancing water stewardship throughout our entire value chain, reducing our water consumption and its intensity across our operations and minimizing water-related risks globally, as well as conserving water resources to maintain good relationships and avoid conflicts with communities. Our dedication extends to improving sustainable water efficiency management practices, encompassing both water withdrawal and discharge. The 3Rs (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle) principle and circular economy concept are adopted by our operations to increase the overall efficiency of water management and to achieve water reduction targets. We are committed to ensuring 100% of our water discharge is treated to improve its quality to below regulatory limit before release. Explore more about our performance in the Water Management section.
Waste Management
Waste is one of our key environmental concerns. We follow the regulations and global standards for waste management as we care about our environmental impact. Our waste management program helps us run our operations efficiently and reduce the amount of waste we produce, following the circular economy concept. Effective waste management begins with meticulous planning, ensuring that our waste management plan prioritizes efficient and cost-effective techniques. This plan encompasses a range of activities, including waste collection, segregation, transportation, reprocessing, recycling, and the disposal of different types of waste while meeting the requirements for health, safety, and infection control. We are currently focused on the proactive reduction of hazardous waste, integrating waste recycled and reused programs, and prioritizing its proper disposal through approved vendors. More than 31,000 training hours highlight our ongoing dedication to responsible waste management practices and sustainable environmental stewardship. Explore more about our performance in the Waste Management section.